APIs and Postman
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are a key part of building many useful applications today. If an application provides an API, it can allow others to build new things with the functionality provided. In this assignment, you will investigate web APIs using Postman. After working with these tools, you will better understand how APIs function, and how you might use them in an application that you build.
Using Postman
When you need to interact directly with APIs, whether creating or consuming them, it is helpful to have a tool to let you see what’s going on with your requests. Postman (https://www.getpostman.com/) calls itself the world’s only complete API Development Environment. I have no way to verify that statement, but I can say that it’s a very useful tool for testing out requests to an API to (a) see what it returns and (b) make sure it returns what you want it to. In this part of the lab, you will use Postman to send some API requests and see how the data is formatted when it comes back.
Setting up
- Go to https://www.getpostman.com/downloads/ and download the version of Postman appropriate for your OS.
- Install the application
- Run Postman on your computer
- You can either choose to create a free Postman account, or you can click the little gray link at the bottom of the window to skip signing up and go straight to the app.
- In the window that appears, choose the option to "Send an API request" by pressing the "New Request" button.
Using a basic API
We’ll start off with the simplest API call possible. It has no parameters, and no authentication. We’ll use the API from https://dog.ceo to get a random picture of a dog.
- In the Request creation screen, enter https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random where Postman asks for the URL.
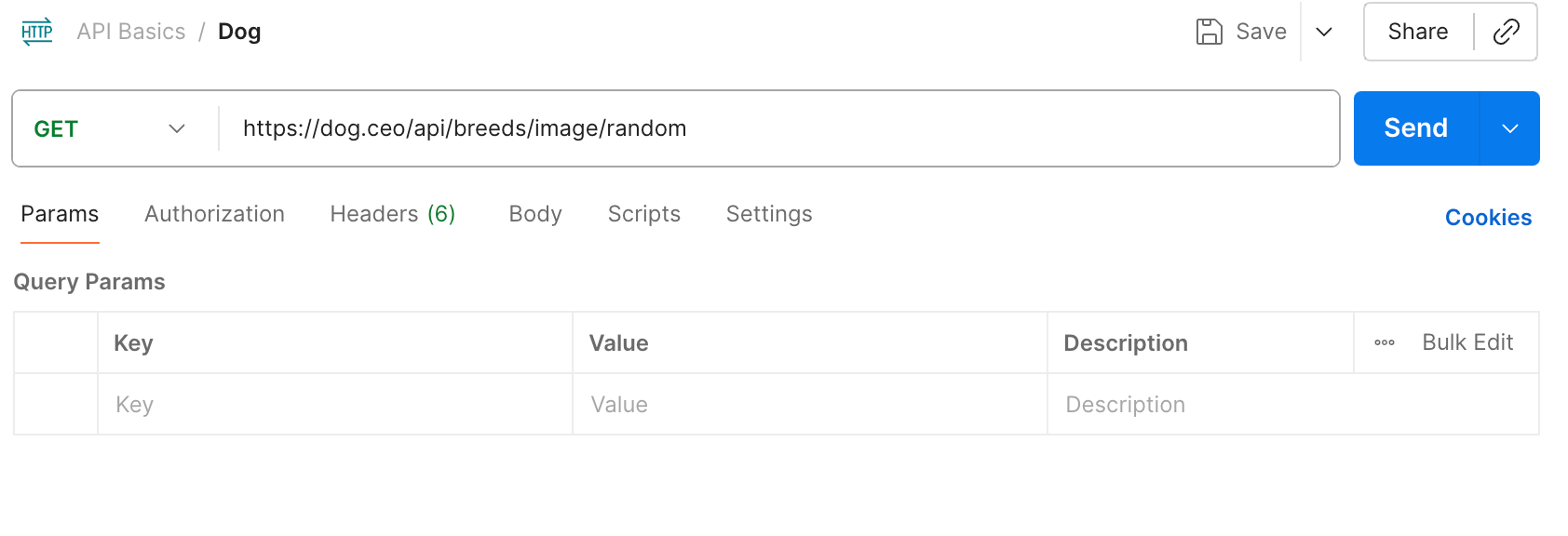
- Click Send to send the request.
- Make sure the request type is "GET" (check the dropdown to the left of the URL)
- In the box at the bottom, you should see the response from the API that includes a single URL. If you copy that URL into a web browser, you’ll see that it’s a picture of a dog, as promised.
GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE are the most common request types used when accessing APIs. These are HTTP request methods, and you can find more information about when to use each here: https://www.w3schools.com/tags/ref_httpmethods.asp.- Visit the API documentation at https://dog.ceo/dog-api/documentation/ to figure out how to get a random photo of a specific dog breed. Update the query in Postman to get 3 pictures of a specific breed (not hounds, since that's the example in the documentation).
POSTing to an API
That was a pretty simple example of a GET API - we're not submitting anything through the API, just pulling information that somebody else is providing for us. Those can be super useful when the information you get from the API is hard to get otherwise - stock prices, weather, sports scores, and many other things can be pulled from APIs into your applications.
But APIs aren't just for getting information - you can also interact with applications and add new information. I've created an example application for exactly this purpose. Visit https://socialdo.is404.net to test it out. Keep this page open so you can see the results of your efforts. Check back as you interact with it through the API.
- In Postman, create a new Request
- Update the request method to
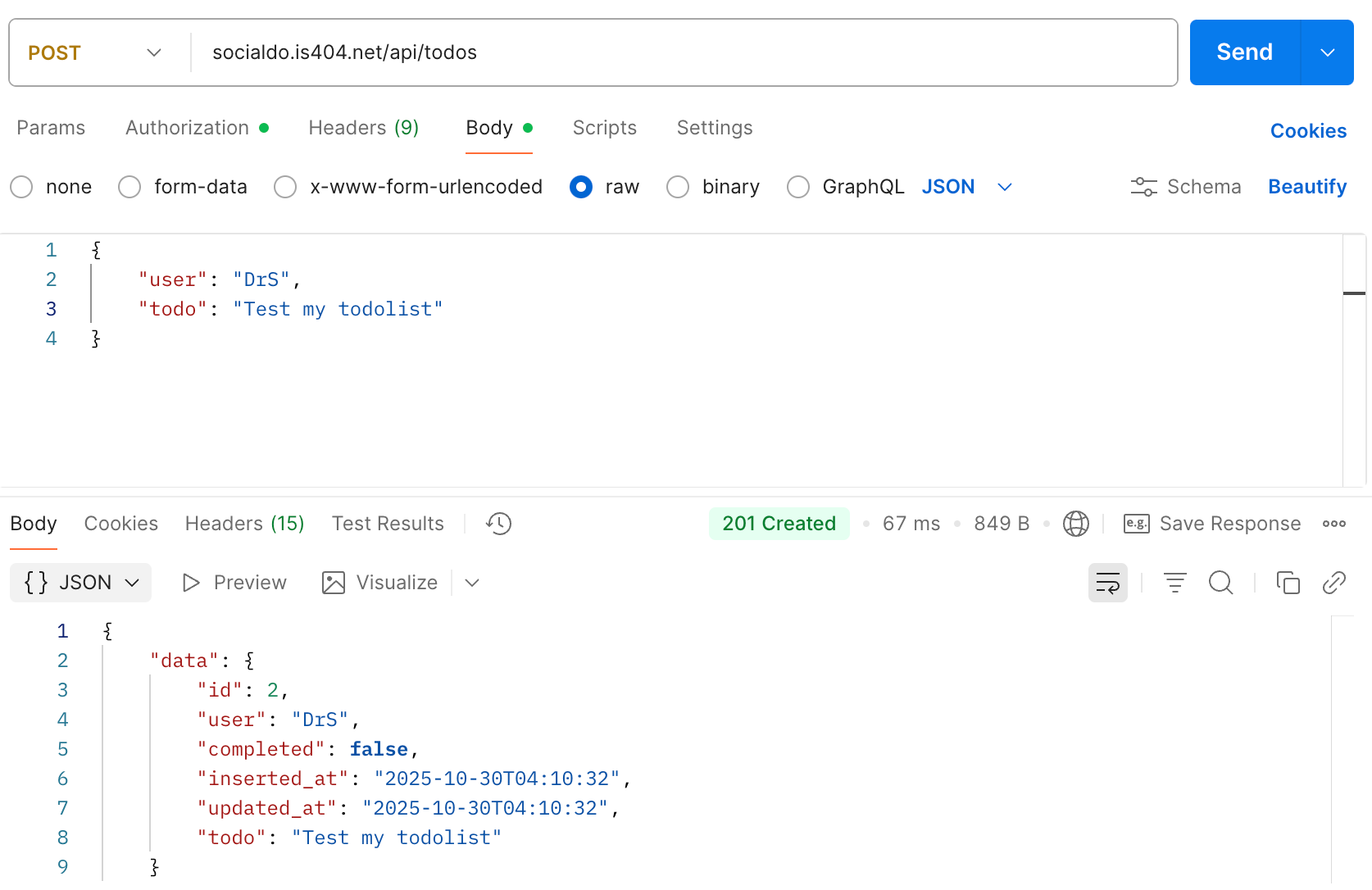
POSTwith the dropdown on the left. - Set the URL to
socialdo.is404.net/api/todos - This API requires authorization with a Bearer token. Go to the Authorization tab, select Bearer Token as the Auth Type, then set the value as
xXBestCoreClassIS404Xx - Click the "Body" tab to set the body of the request that will be sent to the API
- Select "raw"
- In the dropdown on the right, select "JSON"
- Set the value in the box below with keys of "user" and "todo" - you can use whatever you want as the values with those keys. For example, I did:
{
"user": "ProfessorS",
"todo": "Make this website"
}- Send the request - you should get back a JSON object with details about the TODO item you created. You should also see it show up on the homepage (along with your classmates' todos).
Now look through the documentation at https://socialdo.is404.net/docs/api to figure out how to:
- GET a list of todo items for a specific user
- Update (PUT) a todo item to mark it completed
- DELETE a todo item
Interacting with APIs in NodeJS
I use Postman a lot when I'm learning how an API works, because it's an easy way to play around with parameters and other things to get it to do what I want. But the ultimate goal is usually to include an API in an application I'm building. You can pull information from one API into yours, or build your own custom frontend for another application. In fact, many modern web applications are built in exactly this way: APIs on the backend written in Node, Python, or another language, and then a frontend built with React, or an iOS app built with Swift, that talk to the APIs to use the backend's functionality.
The code below is just one example of using the built-in fetch library to pull data from the SocialDo API. You can also create custom functions to POST, PUT, or DELETE using fetch or the popular axios library for NodeJS. Put this code into an app you're working on, and run it to see how it works. Modify the code to pull data for a single user, then create a new page to create a new todo item with the POST endpoint.
// server.js
import express from "express";
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.get("/todos", async (req, res) => {
try {
const response = await fetch("https://socialdo.is404.net");
const json = await response.json();
const todos = json.data;
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>TODO List</title>
<style>
body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; padding: 20px; }
ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; }
li { margin: 8px 0; }
strong { color: #333; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>TODOs</h1>
<ul>
${todos
.map(
(item) => `<li><strong>${item.user}</strong>: ${item.todo}</li>`
)
.join("")}
</ul>
</body>
</html>
`;
res.send(html);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
res.status(500).send("Error fetching TODOs");
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});Other APIs
Now that you know the basics of how to GET and POST, it's time to explore a bit. Head to https://free-apis.github.io and search for some APIs to get information that is useful or interesting to you.